New research reveals significant contribution by cathedrals to local economies and communities
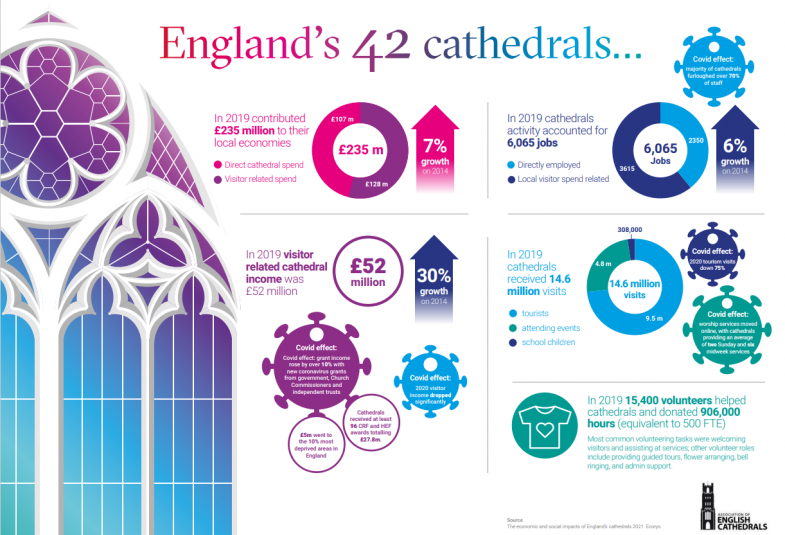 A new report has highlighted the hugely positive economic and social impact England’s cathedrals have on the cities and communities they serve and the effect the pandemic has had on their contribution. In 2019, England’s 42 Anglican cathedrals contributed £235m to their local economies. They provided 6,065 jobs full time equivalent jobs and volunteering posts for 15,400 people who gave 906,000 hours of their time. They welcomed more than 14.6 million visits, 308,000 by schoolchildren for educational events, and 9.5m from tourists.
A new report has highlighted the hugely positive economic and social impact England’s cathedrals have on the cities and communities they serve and the effect the pandemic has had on their contribution. In 2019, England’s 42 Anglican cathedrals contributed £235m to their local economies. They provided 6,065 jobs full time equivalent jobs and volunteering posts for 15,400 people who gave 906,000 hours of their time. They welcomed more than 14.6 million visits, 308,000 by schoolchildren for educational events, and 9.5m from tourists.
In the same year, cathedrals hosted a rich programme of arts, music, heritage and culture – amounting to 9,580 events equivalent to two every three days – as well as providing the venues for film shoots such as The Crown, Doctor Who and Avengers:Endgame.
They played a huge role socially, responding to local need by running foodbanks, support groups for the more vulnerable, the unemployed, the homeless, outreach activities in schools, residential homes and hospitals, lunch clubs, parent and toddler groups, and community cafes. And over two thirds of cathedrals are part of the A Rocha Eco Church programme, helping the Church of England achieve its carbon reduction targets by 2030.
The Economic and Social Impact of Cathedrals in England was produced by independent research consultancy, Ecorys, for The Association of English Cathedrals to show how cathedrals use their assets to promote mission and well-being. This latest research builds on previous studies of 2004 and 2014 and continues to prove that cathedrals successfully provide a multitude of community focussed services alongside worship. It enables cathedrals to demonstrate their social and economic impact as good stewards of their buildings, their history, their musical and spiritual inheritance, and, as good servants of their communities, to the wider church, local and national government, and other stakeholders.
Evidence collected on the impact of COVID-19 - which saw Government mandated closures and restrictions on gatherings - reveals visitor numbers slumped by 75 per cent compared to 2019, visitor spend was down proportionately, and over 70 per cent of cathedral staff were furloughed.
The research continues, stating that the fall in visitor numbers has had a significant effect on cathedrals’ income levels, particularly those cathedrals more dependent on the visitor economy.
It also found a significant fall in cathedrals’ average non-visitor income, driven by a reduction of almost 80% in income generated from the use of cathedral facilities. Closure and restrictions on congregation size also meant fewer people attended services in the cathedral, down from a midweek average of 362 adults and 108 children in 2019, to 84 and 25 respectively in 2020, leading, inevitably, to a drop in congregational giving.
But the research also found that COVID-19 had given rise to new pastoral and creative opportunities. While 75 percent of cathedrals’ existing social projects stopped due to closures and restrictions, new services like food deliveries, shopping and online face to face pastoral support developed.
From 2020, worship services moved online with cathedrals providing on average two Sunday services and six midweek services, and digital technologies enabled cathedrals to reach more people with creative online initiatives such as prayer walls, candle lighting, tours, pilgrim trails, and some, like Salisbury Cathedral, took a major art exhibition online.
In Durham, a new community of worshippers, the Community of Prayer, was born out of the growing online community of worshippers that formed around its live-streamed Daily Offices and Sunday Eucharists which started in the first lockdown.
In conclusion, the study found clear evidence that cathedrals make a significant contribution to their local economies and have a positive impact on their local communities, consistent with the findings in 2014 and 2004.
It also found that the pandemic, while bringing fresh creative opportunities, has brought about a number of challenges, particularly in the form of reduced visitor numbers, which has had a significant effect on cathedrals’ income levels and a direct impact on cathedrals’ ability to be self-sustaining in 2020. Cathedrals estimate their finances will be constrained for some time to come while national and local economies recover.
It recommends further research into how cathedrals are being affected by COVID-19, including any knock-on impact on cathedrals’ ability to continue offering pre-COVID levels of support to their local communities.
Source: churchofengland.org

